There is always new developments with pharmaceutical manufacturing technology. Efficient and reliable gas filtration is the basis for all stages of pharmaceutical production, protecting drug quality and ultimately ensuring patient safety. The vent filters, mainly the air filters, are used in many scenarios such as single-use system, fermentation tanks, and WFI (water for injection).
In biological products, it involves many fields such as antibody industry, genetic engineering, recombinant protein engineering and cell engineering. From the recovery of microorganisms to the terminal sterilizing filtration, gas filters have always been with the production, and sterilizing grade gas filters are the top priority.
In this article, we explain the feature and benefits of different venting membrane specifications from
Single-use System Vent
Gamma-compatible APBB series membrane
Application: Single-use system
Advantage: PVDF, Gamma-compatible and autoclavable
The application of single-use systems (SUS) can promote the rapid development of biological products, and is now the first choice for many biopharmaceutical companies. It’s applied to bioreactors, intermediate product transportation and storage, and final sterile filtration. Since most SUS adopt gamma radiation sterilization, where sterilizing vent filter is a crucial component, gamma compatibility is an important feature of sterilizing vent filters for SUS.
Cobetter-APBB series sterilizing vent filters adopt Gamma compatible hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane material which can be integrated into filter cartridges and capsules, providing convenient and safe use of our single-use products.
Fermentation Tank Vent:
Strong-hydrophobic, High-throughput AFMB series membrane
Application: Fermentation tank vent
Advantage: Autoclavable, long life time
The use of stainless-steel storage tanks for microbial fermentation is a traditional process of biopharmaceutical manufacturing. To ensure that fermented products are not infected by natural bacteria and other microorganisms, the vent matching the fermentation tank is particularly important. It is equivalent to the lungs of microorganisms and ensures the purity and continuous replication of microorganisms.

Sterile Compressed Air Application
Hydrophobic and oleophobic AFBB series membrane
Application: Sterile compressed air
Advantages: Steam sterilization, hydrophobic and oleophobic
When carrying out large-scale biological fermentation, the ventilation volume requirement of microorganisms has far exceeded the ventilation volume of the vent. In this situation, it is necessary to use multiple air sterilization filters in parallel, so as to provide microorganisms with a higher flow rate of sterile air to meet their growth. However, a small amount of oil will inevitably be introduced when the compressor is working. Since a large amount of compressed air passes through the gas sterilization filter, the traditional gas sterilization filter is hydrophobic and is easily contaminated by oil in the compressed air.
Cobetter-AFBB series gas sterilization filters adopt hydrophobic and oleophobic PTFE membranes, which can effectively prevent water and oil from contaminating the air sterilization filter and extend its service life.
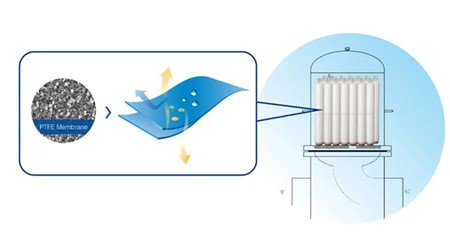
WFI (water for injection) Tank Vent
High temperature resistant HSGPFP series membrane
Application: Water for injection tank vent
Advantages: Steam sterilization, resistant to long-term high temperature use
WFI is the most commonly used solution in pharmaceutical processes, and its storage tank temperature is kept between 80 and 90°C. To ensure the balance of internal and external pressure in the storage tank and internal cleanliness at high temperatures, the matching vent is essential for the storage tank.
The support membrane made of traditional polypropylene (PP) cannot withstand long-term high-temperature use, therefore the support of Cobetter HSGPFP series membrane is made of high-temperature-resistant polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) material, which can be used in high-temperature and humid environments to delay high-temperature aging.


